Nutrient management in agriculture focuses on optimizing the use of crop nutrients to enhance productivity and safeguard the environment.
The fundamental concept of nutrient management revolves around harmonizing soil nutrient inputs with the specific requirements of the crops.
Nutrient Management
In the realm of agriculture and gardening, nutrient management plays a vital role in ensuring the health and productivity of plants.
By understanding the essential nutrients plants require and how to effectively supply them, growers can optimize their growing conditions and harvests.
This article discusses nutrient management, exploring its key concepts and practical tips for maximizing plant growth.
The Importance of Nutrients for Plant Growth
Plants require a range of nutrients to support their growth and development.
These essential nutrients can be categorized into macronutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, and micronutrients, including iron, zinc, and manganese.
Each nutrient plays a specific role in plant health, from supporting photosynthesis to enhancing disease resistance.
Macronutrients
Nitrogen: Essential for leaf and stem growth.
Phosphorus: Key for root development and flowering.
Potassium: Aids in overall plant health and disease resistance.
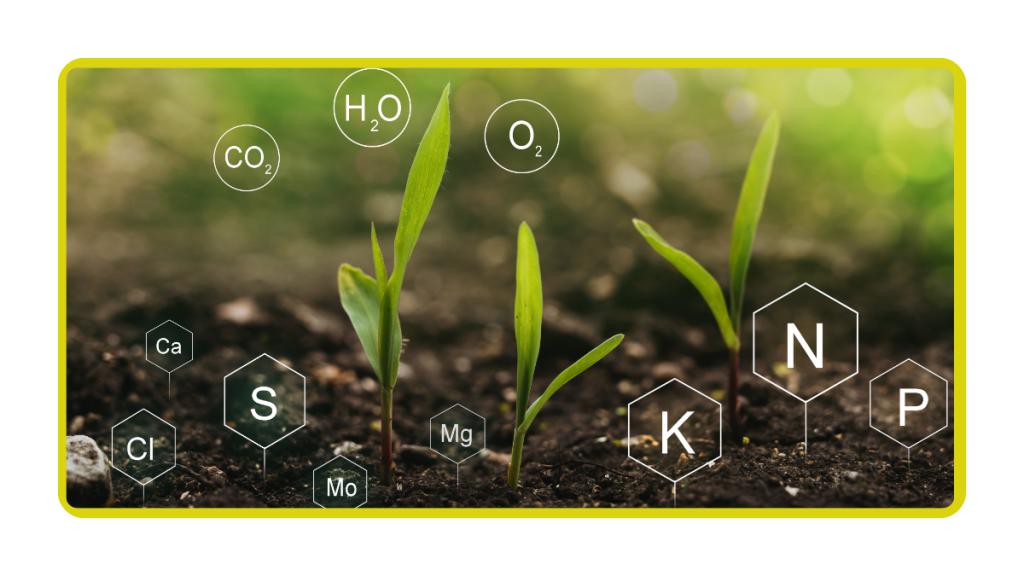
Micronutrients
Iron: Required for chlorophyll production.
Zinc: Supports enzyme function and hormone regulation.
Manganese: Plays a role in photosynthesis and nutrient uptake.
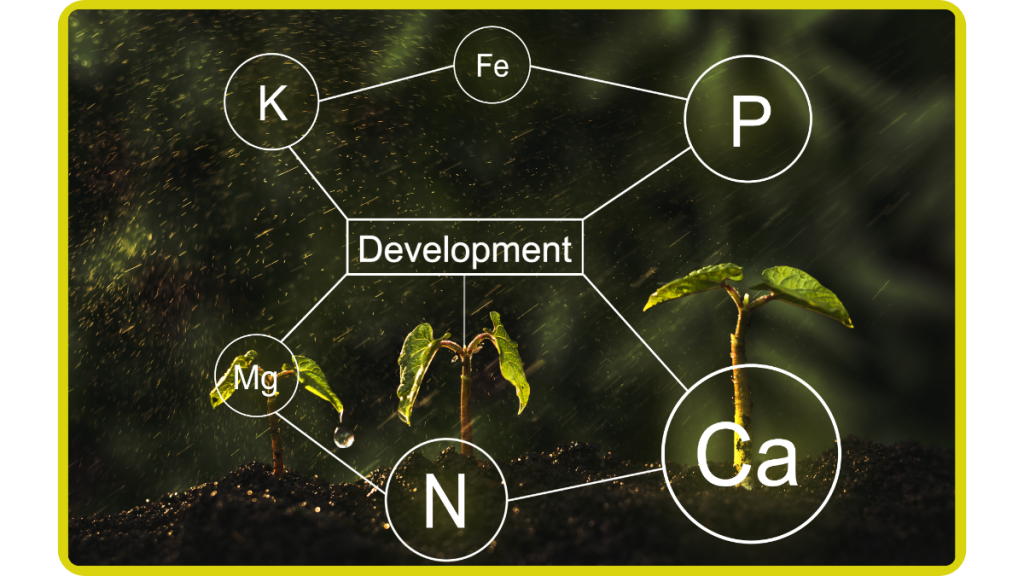
Nutrient Deficiency and Excess
Understanding the signs of nutrient deficiency or excess in plants is crucial for effective nutrient management.
Symptoms such as yellowing leaves, stunted growth, or leaf burn can indicate an imbalance in nutrient levels.
Soil tests and visual inspections can help identify deficiencies or excesses, allowing growers to take corrective actions.
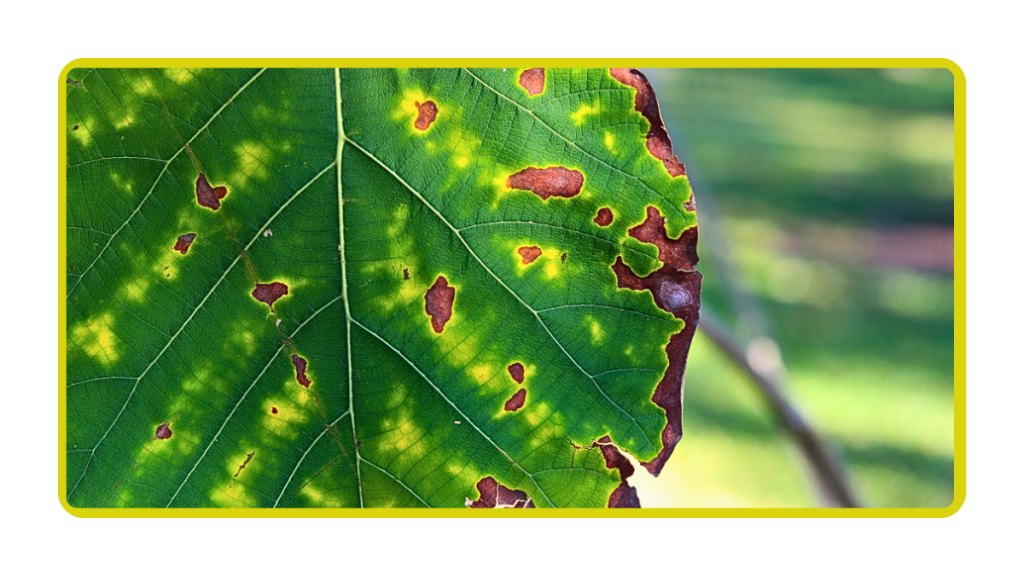

Signs of Nutrient Deficiency
- Yellow or discolored leaves.
- Poor growth or stunted development.
- Leaf curling or distortion.
- Signs of Nutrient Excess:
- Leaf burn or scorching.
- Reduced flowering or fruiting.
- Wilting despite adequate watering.
Implementing Effective Nutrient Management Strategies
To ensure plants receive the right balance of nutrients, growers can implement various nutrient management strategies.
These include soil testing, fertilization schedules, and targeted nutrient applications based on plant needs.
By monitoring nutrient levels and adjusting practices accordingly, growers can promote optimal plant health and productivity.
Soil Testing
Regular soil testing helps determine the pH levels and nutrient content of the soil, allowing for tailored nutrient management plans.
Fertilization Schedules
Establishing consistent fertilization schedules based on plant growth stages can help maintain nutrient availability throughout the growing season.
Targeted Nutrient Applications
Applying specific nutrients based on plant requirements, such as foliar sprays or root drenches, can address deficiencies more effectively.
Conclusion
Nutrient management is a fundamental aspect of successful plant growth and cultivation.
By understanding the importance of essential nutrients, recognizing signs of deficiency or excess, and implementing effective management strategies, growers can optimize their growing conditions and achieve thriving plant growth.
By prioritizing nutrient management, individuals can foster healthy, vibrant plant life and reap the rewards of bountiful harvests.
Here is a comprehensive guide to Integrated Nutrient Management.
Learn about how to get started with Nutrition Management.

